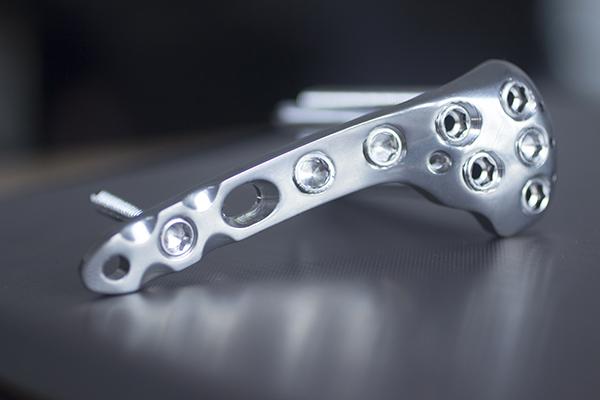
Meeting the Challenges of Medical Machining.
In 2022, there was a 14% increase in hip and knee replacements over the previous year. As the average age of the population of the USA and other developed nations increases, so does the demand for a wide range of orthopedic implants, surgical instruments, medical molds, and other medical devices.
But machining components for the medical industry can be a challenging endeavor. Here are four things to keep in mind when evaluating new opportunities in the medical machining field.
Growth is expected. So is change.
As procedures increase, manufacturers will develop new and innovative products to deliver better outcomes and maintain their competitive edge. Suppliers of machined medical components must be ready to meet the demands for increased volumes, multiple part sizes, and more frequent part design changes. Flexibility in both machining technology and processes is key.
Exotic materials are commonplace.
Materials used in implants, surgical tools, and other medical devices face demands that products in other industries do not. They must meet strict mechanical and biocompatibility requirements, and stainless steels, titanium, cobalt alloys, magnesium, ceramics, polymers, and composites are all on the (surgical) table. Understanding the ins-and-outs of machining a wide range of materials—and having the equipment to machine them—is essential for getting ahead.
Surface finishes are critical.
Medical implants, surgical tools, and molds for medical devices all demand high-quality surface finishes. The right machines, controls, workholding, tooling, and cutting strategies can reduce or eliminate the need for secondary finishing processes, helping medical machining shops to deliver precise parts profitably.
Get it done in one.
With extremely tight dimensional accuracy requirements and the above mentioned surface finish challenges, multiple part setups can be a quality and productivity killer. Thankfully, there are a wide range of machine tools, from 5-axis machining centers to swiss-style lathes, with advanced tooling that can produce some of the most complex parts in a single setup.
So, how can you be prepared to take advantage of current opportunities and ready your business for the future?
First, invest in the right machining technology. In the highly-competitive medical parts manufacturing industry, having the right machine tools and processes are critical for success. When you’re adding new equipment, make sure to not just look at increasing your capacity, but augmenting your shop floor with machines that can deliver the high precision parts, critical surface finishes, and flexibility that medical device production demands.
Second, partner with companies that have charted this path before. This is our not-so-subtle plug for Ellison Technologies (you’re visiting our website; what were you expecting?). We’ve been in business since 1955 and have a long track record in helping medical device manufacturers achieve their goals. We work with our carefully cultivated list of vendor partners to bring tailored medical machining technology and turnkey solutions to your shop floor. Ellison Technologies has offices in 16 cities, staffed with applications engineers that are ready to help you Make More.
Medical Articles & Customer Stories
Doosan - CNC Manufacturing
Wagner Machine
Wagner Machine
"We wanted to increase part diameter capacity and raise productivity."
-Kurt Wagner
Doosan - Precisionmatics
Precisionmatics
Precisionmatics
"With this machine, we can be competitive in smaller run, complex work."
-Steve Pustay

Wagner Machine
Wagner Machine
"We wanted to increase part diameter capacity and raise productivity."
-Kurt Wagner
Medical Applications, Meet Medical Solutions. STAT!
Most medical machining applications are a unique combination of exotic materials, complex geometries, tight tolerances, and varying production volumes. Here is a sample of a few applications and the technology that we provide our customers to help make them, as well as some additional considerations to keep in mind.
Application Name:
Suture button
Materials:
Medical grade PEEK (polyether ether ketone) and titanium
Application Name:
Suture button
Materials:
Medical grade PEEK (polyether ether ketone) and titanium
Application Notes:
Suture buttons are relatively simple parts, and streamlining production is critical for profitability. Manufacturing these on a Swiss lathe rather than a conventional lathe can dramatically reduce cycle times.

Tulip
Suture button
Materials:
Stainless steel, titanium, and medical grade PEEK (polyether ether ketone)
Tulip
Suture button
Materials:
Stainless steel, titanium, and medical grade PEEK (polyether ether ketone)
Application Notes:
Tulip heads (AKA polyaxial pedicle screw heads) require ID and OD turning as well as internal threading and cross holes. A properly equipped Swiss lathe can quickly deliver the tight tolerances and surface finishes that these parts demand.

Application Name:
Fracture plate
Materials:
Stainless steel, titanium, and medical grade PEEK (polyether ether ketone)
Application Name:
Fracture plate
Materials:
Stainless steel, titanium, and medical grade PEEK (polyether ether ketone)
Application Notes:
Conventional machining fracture plates (AKA bone plates) would require multiple operations, but these components are made in a single setup on Swiss lathes.

Application Name:
Spine plate
Materials:
Stainless steel, titanium, and medical grade PEEK (polyether ether ketone)
Application Name:
Spine plate
Materials:
Stainless steel, titanium, and medical grade PEEK (polyether ether ketone)
Application Notes:
Similar to fracture plates, spine plates can be more quickly and precisely made on Swiss lathes. Avoiding the multiple setups of conventional machining not only improves cycle times, but offers higher precision as well.

Application Name:
Bone screw
Materials:
Stainless steel and titanium
Application Name:
Bone screw
Materials:
Stainless steel and titanium
Application Notes:
Bone screws come in a wide range of sizes and lengths, so being able to switch between setups quickly is critical for profitability. A Swiss lathe with dual thread whirling capabilities and specialty accessories for long part extractions delivers the ultimate in flexible production.
Learn more about how Ellison can help you succeed in the Medical Industry. Contact Us Today!

MEDICAL MACHINING
BOLSTER REVENUE AND REPUTATION WITH ELLISON EXPERTISE BY YOUR SIDE
MEDICAL MACHINING
BOLSTER REVENUE AND REPUTATION WITH ELLISON EXPERTISE BY YOUR SIDE
- Enjoy added efficiency and accuracy
- Increase shop capabilities
- Implement next-level automation
- Reap the benefits of 24/7 production
- Chart a path for lasting growth and success

